Introduction: The Essence of Life
Water makes up 60% of your body weight and is involved in nearly every biological process. Yet studies show 75% of Americans are chronically dehydrated, leading to fatigue, headaches, and even long-term health consequences.
This comprehensive guide will explore:
- The vital roles water plays in your body
- Surprising signs of dehydration
- How much water you really need
- Creative ways to stay hydrated
- The truth about hydration myths
Why Your Body Craves Water
1. Cellular Functions
- Delivers nutrients to cells
- Removes waste products
- Facilitates chemical reactions
2. Physical Performance
- Just 2% dehydration reduces:
- Endurance by 20%
- Strength by 10%
- Reaction time by 30%
3. Cognitive Function
- Dehydration causes:
- Brain shrinkage (temporary)
- Poor concentration
- Increased perception of task difficulty
4. Digestive Health
- Prevents constipation
- Supports gut microbiome
- Aids nutrient absorption
5. Temperature Regulation
- Sweat cools the body
- Prevents heat stroke
- Maintains stable core temperature
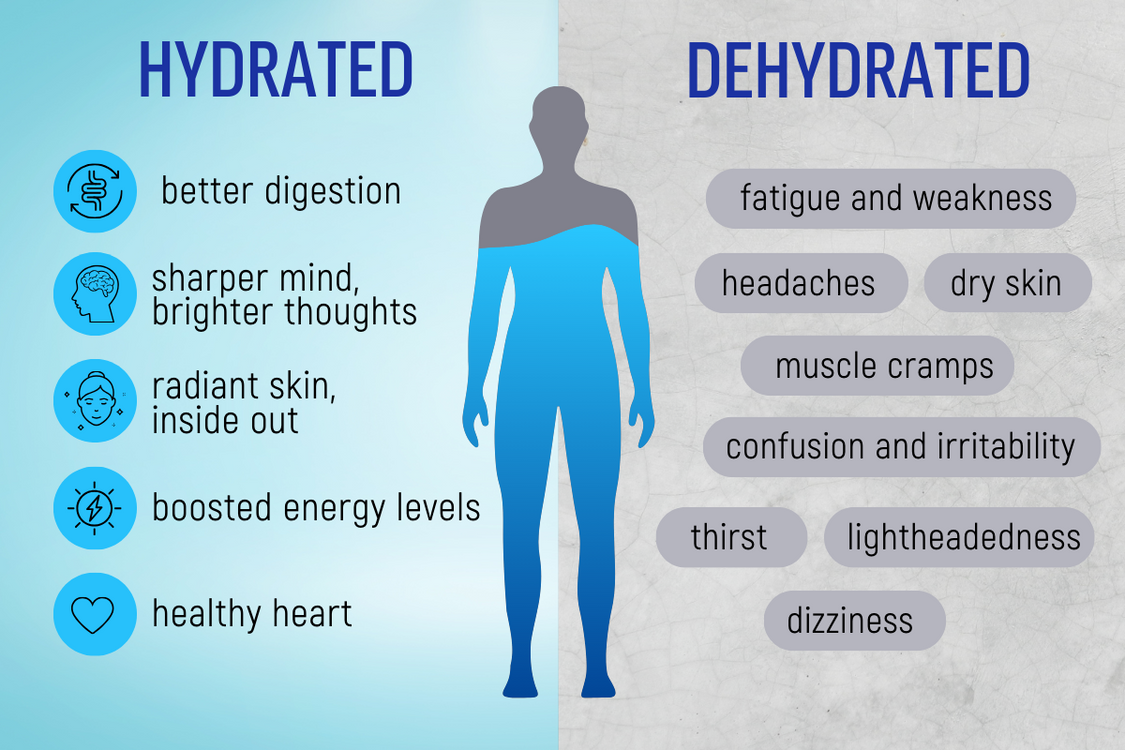
Are You Dehydrated? 8 Warning Signs
- Dark yellow urine (should be pale straw color)
- Dry mouth/skin
- Fatigue or dizziness
- Headaches
- Muscle cramps
- Brain fog
- Bad breath
- Food cravings (often confused with hunger)
Quick Test: Pinch the skin on your hand. If it doesn’t snap back quickly, you may be dehydrated.
How Much Water Do You Really Need?
The Truth About the 8×8 Rule
While the “8 glasses daily” is easy to remember, individual needs vary based on:
- Body weight (divide weight in pounds by 2 = ounces needed)
- Activity level (add 12 oz per 30 minutes of exercise)
- Climate (hot/humid = more fluids)
- Diet (water-rich foods count too)
Pro Tip: Check your urine color throughout the day – it’s the best hydration indicator.
Beyond Plain Water: 5 Hydrating Alternatives
- Herbal Teas (caffeine-free)
- Infused Waters (try cucumber-mint or lemon-ginger)
- Coconut Water (natural electrolytes)
- Sparkling Water (great for soda cravings)
- Water-Rich Foods:
- Cucumber (96% water)
- Watermelon (92%)
- Strawberries (91%)
Hydration Myths Debunked
❌ Coffee dehydrates you
Truth: Moderate caffeine has minimal diuretic effect
❌ You can’t drink too much water
Truth: Hyponatremia (water intoxication) is dangerous
❌ Thirst means you’re already dehydrated
Truth: Thirst is an early warning system
❌ Sports drinks are always best
Truth: Only needed for intense exercise >1 hour
Special Hydration Considerations
For Athletes
- Drink 16-20 oz 2 hours before exercise
- 7-10 oz every 10-20 minutes during
- Replenish with electrolytes after intense sessions
For Seniors
- Reduced thirst sensation
- Higher dehydration risk
- May need reminders to drink regularly
For Kids
- More susceptible to dehydration
- Encourage fun water bottles
- Watch for signs during play
Making Hydration a Habit
10 Simple Strategies
- Start your day with a glass of water
- Carry a reusable water bottle
- Set hourly phone reminders
- Drink before meals
- Flavor water naturally with fruits
- Track intake with apps
- Eat more water-rich foods
- Alternate alcoholic drinks with water
- Choose sparkling over soda
- Notice your urine color
When to Seek Medical Help
Consult a doctor if you experience:
- Extreme thirst that won’t quit
- Little/no urination
- Dizziness/confusion
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sunken eyes (in children)
These could indicate severe dehydration requiring IV fluids.
Conclusion: Your Liquid Lifeline
Water isn’t just about quenching thirst – it’s the foundation of every bodily function. By tuning into your body’s needs and developing smart hydration habits, you can boost your energy, sharpen your mind, and support long-term health.